Health Alert: Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Outbreak in Delaware County
Delaware County residents are urged to be vigilant after a recent surge in hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) cases. This highly contagious viral infection, primarily affecting young children, is causing concern among health officials. This article provides crucial information about HFMD, its symptoms, prevention, and what Delaware County residents should do to protect themselves and their families.
Understanding Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
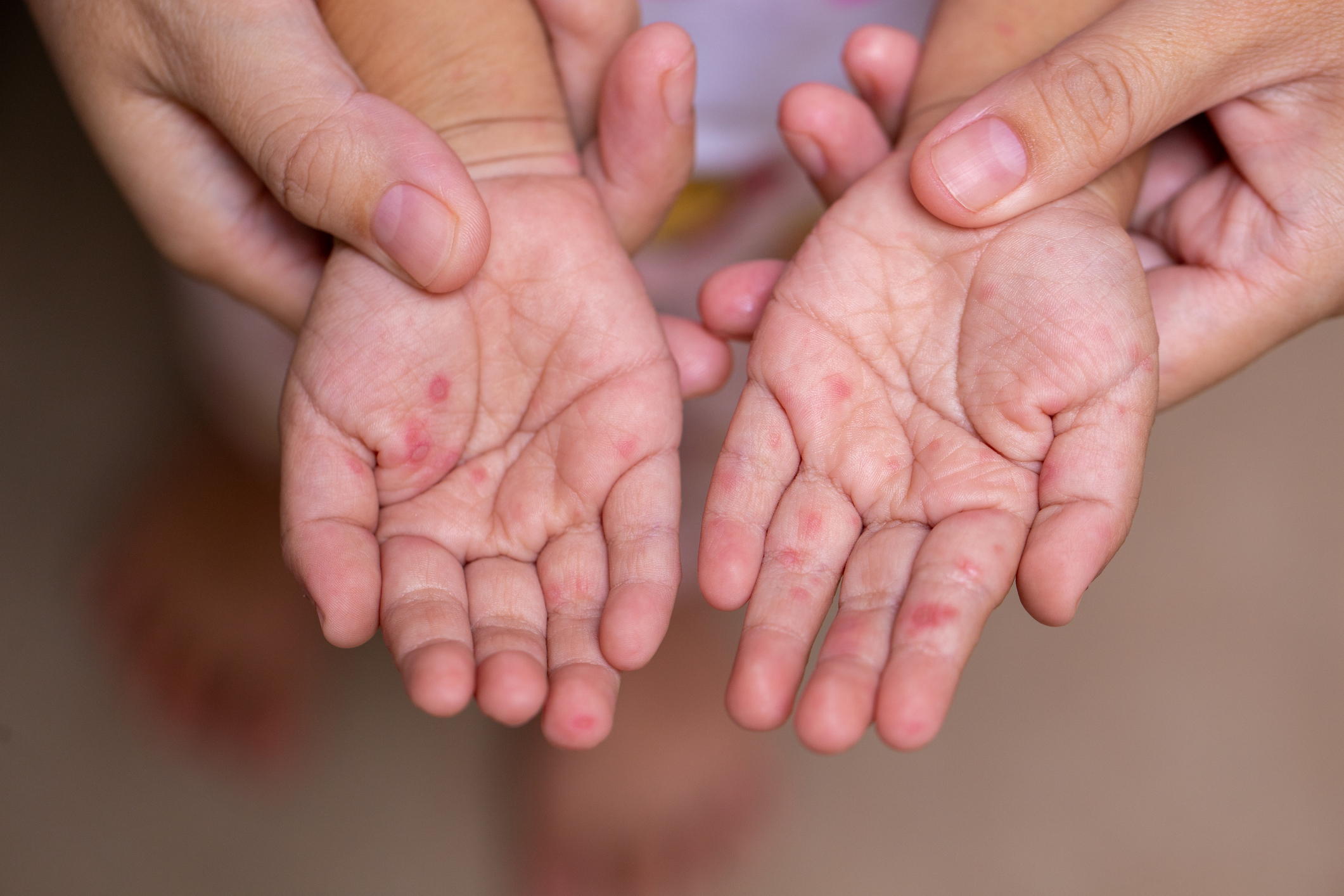
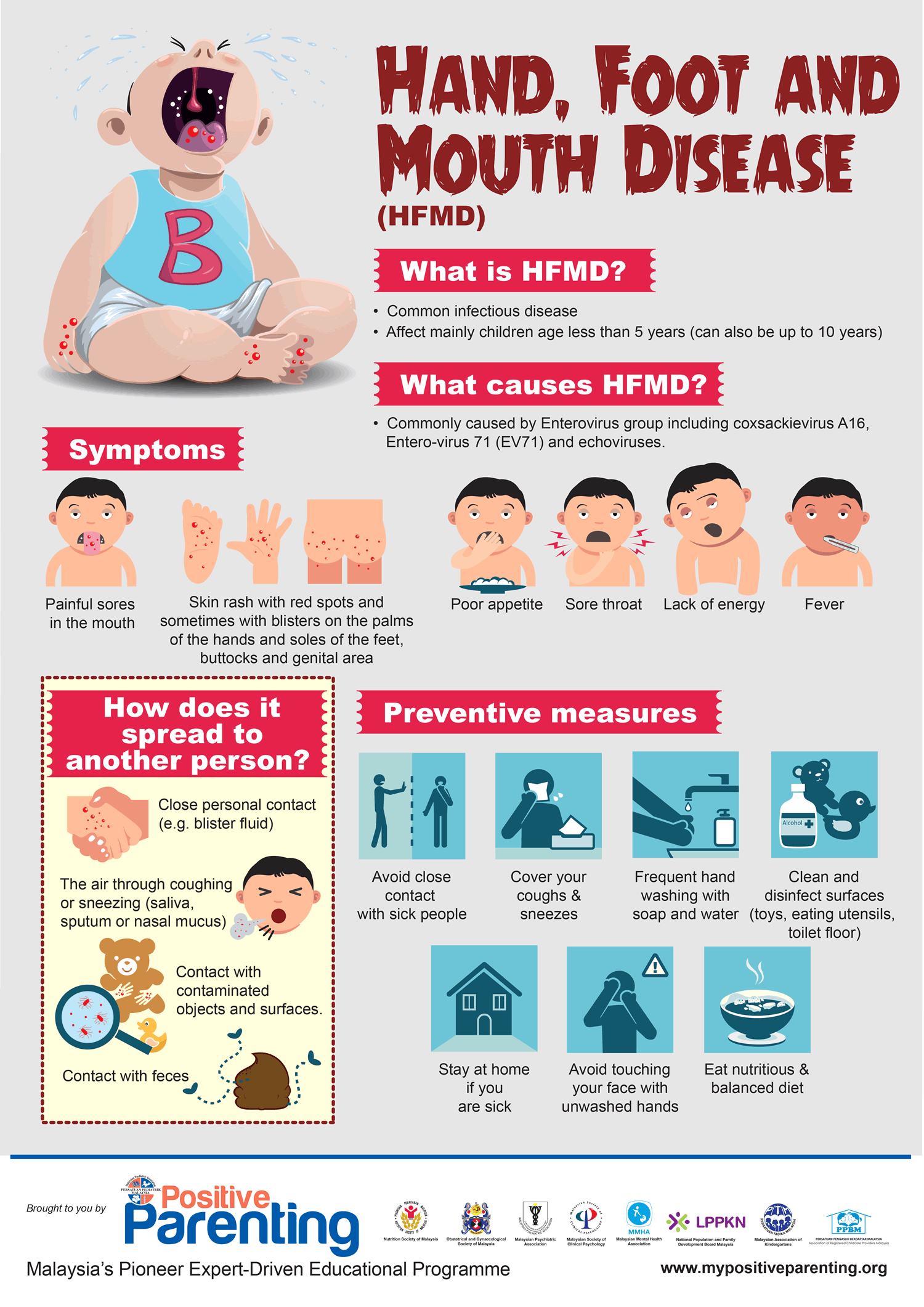
HFMD is a common viral illness, most often caused by Coxsackievirus A16 and Enterovirus 71. While typically mild, it can be quite uncomfortable and, in rare cases, lead to complications. The disease is easily spread through:
- Direct contact: Touching an infected person’s nose, mouth, or throat secretions.
- Indirect contact: Touching surfaces contaminated with the virus, then touching your mouth or nose.
- Respiratory droplets: Inhaling droplets produced by an infected person’s cough or sneeze.
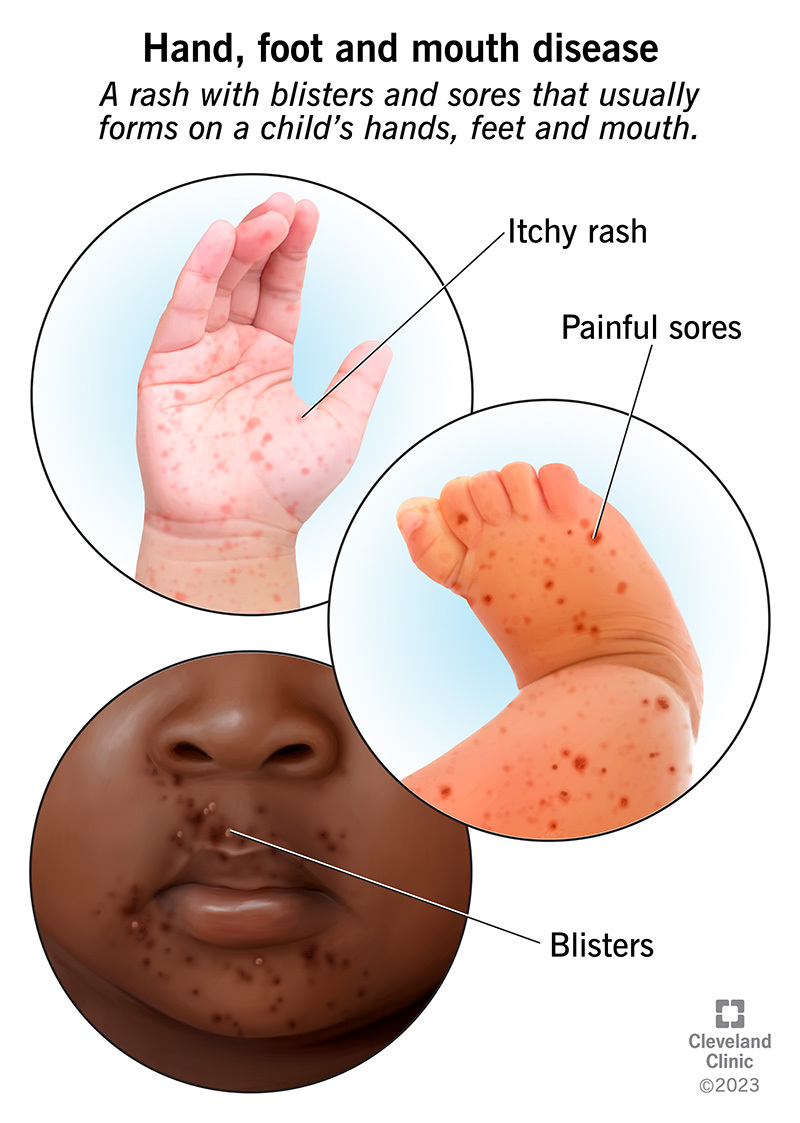
Symptoms of HFMD
Recognizing HFMD symptoms is crucial for early intervention and preventing its spread. Common symptoms include:
- Fever: Often the first symptom to appear.
- Sore throat: Can be accompanied by difficulty swallowing.
- Mouth sores: Painful, blister-like sores inside the mouth, on the tongue, and gums.
- Rash: A characteristic rash appears on the hands, feet, and sometimes the buttocks and knees. The rash typically consists of small, flat or slightly raised red spots.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most HFMD cases resolve on their own within 7-10 days, seek medical attention if:
- Your child experiences severe dehydration.
- Your child has difficulty breathing.
- Your child’s fever is unusually high or persistent.
- Your child shows signs of neurological involvement (e.g., lethargy, stiff neck).
Preventing the Spread of HFMD in Delaware County
Prevention is key to controlling the spread of HFMD. Delaware County residents are advised to:
- Practice good hygiene: Frequent and thorough handwashing with soap and water is crucial. Hand sanitizer can be used when soap and water are unavailable.
- Avoid close contact: Limit contact with individuals who are exhibiting symptoms of HFMD.
- Disinfect surfaces: Regularly disinfect frequently touched surfaces, such as doorknobs, toys, and countertops.
- Stay home when sick: Keep children home from school or daycare if they are exhibiting symptoms of HFMD.
Delaware County Health Department Response
The Delaware County Health Department is actively monitoring the situation and working to contain the outbreak. They are providing updates and resources to the community through their website and social media channels. Residents are encouraged to check the official website for the latest information and guidance.
Conclusion
The recent increase in HFMD cases in Delaware County highlights the importance of vigilance and preventative measures. By understanding the symptoms, practicing good hygiene, and following the recommendations of the Delaware County Health Department, residents can help protect themselves and their communities from this contagious illness. Remember, early identification and prompt action are crucial in managing HFMD outbreaks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is HFMD dangerous?
A1: While usually mild and self-limiting, HFMD can cause discomfort and, in rare cases, lead to serious complications. Seek medical attention if you observe severe symptoms.
Q2: How long is someone contagious with HFMD?
A2: Individuals are typically contagious from the onset of symptoms until the sores have completely healed, which usually takes about a week to ten days.
Q3: Is there a vaccine for HFMD?
A3: Currently, there is no vaccine available for HFMD. Prevention relies on good hygiene and avoiding contact with infected individuals.
Q4: What kind of treatment is available for HFMD?
A4: Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, such as fever and pain relief. Over-the-counter pain relievers (like acetaminophen or ibuprofen) can help alleviate discomfort. Keeping the child hydrated is also very important.
Q5: Where can I find more information about the Delaware County outbreak?
A5: Visit the official website of the Delaware County Health Department for the latest updates, advisories, and resources. You can also contact your local health provider with any concerns.