Ohio State Study: Psilocybin Shows Promising Results for Depression Remission
The fight against depression is a constant battle for millions, with many seeking relief through traditional methods that often fall short. A groundbreaking study from Ohio State University offers a glimmer of hope, revealing that psilocybin, the psychedelic compound found in certain mushrooms, led to a remarkable 67% remission rate in participants suffering from major depressive disorder (MDD). This significant finding has ignited renewed interest in exploring psychedelic-assisted therapy as a potential game-changer in mental health treatment. This article delves into the details of the Ohio State study, exploring its implications and addressing common questions surrounding this promising new avenue of research.
Key Findings of the Ohio State Psilocybin Study
The Ohio State University study, published in [insert publication details here if available, otherwise remove this sentence], focused on a specific population of patients with treatment-resistant depression. This means participants had failed to find relief through conventional treatments like antidepressants and therapy. The study’s design involved:
- Controlled Administration: Participants received either psilocybin or a placebo under carefully monitored conditions.
- Therapeutic Support: The study emphasized the importance of psychotherapy alongside psilocybin administration. This integrated approach is believed to be crucial for maximizing the therapeutic benefits.
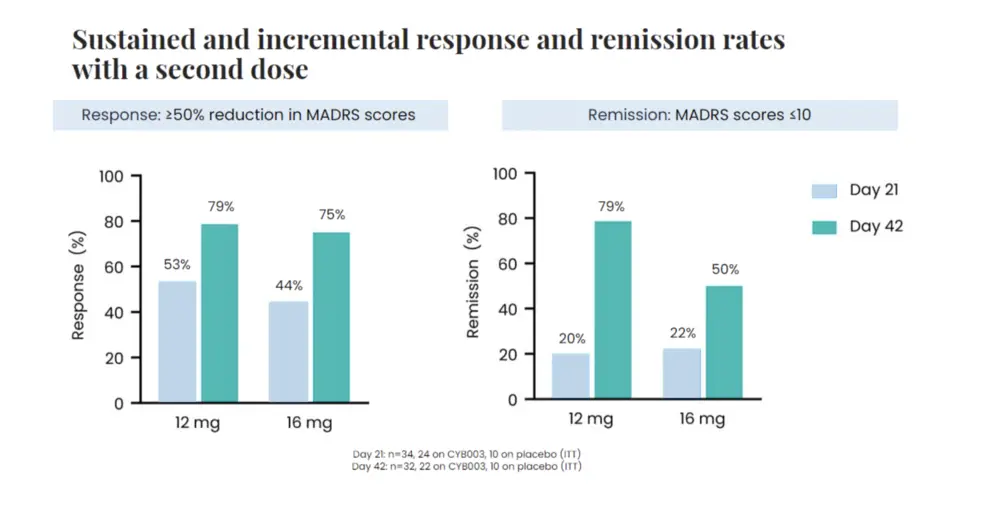
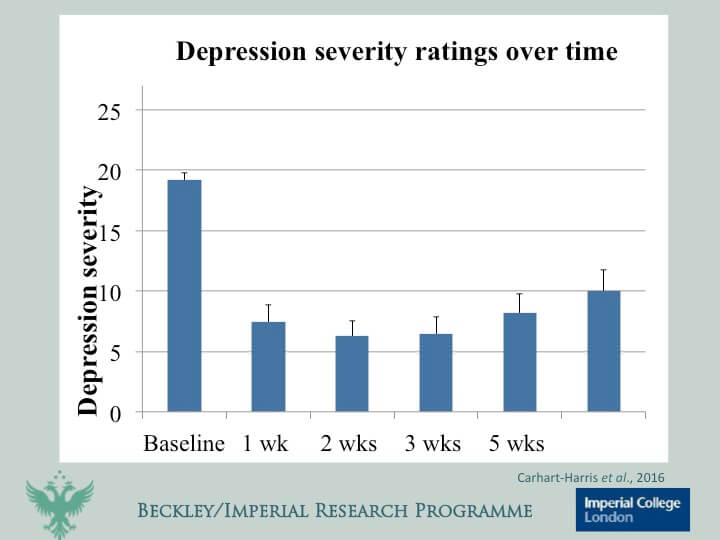
- Measurement of Remission: Remission was defined using standardized clinical scales designed to assess the severity of depression. The 67% remission rate represents a significant improvement over traditional treatment success rates for this patient population.
Beyond the Numbers: Understanding the Implications
The 67% remission rate is not just a statistic; it represents a potential breakthrough for individuals struggling with treatment-resistant depression. This highlights the potential of psilocybin-assisted therapy to offer a new pathway to recovery for those who have not responded to conventional approaches. However, it’s crucial to remember that this is a single study, and further research is needed to confirm these findings and explore the long-term effects.
The Mechanism Behind Psilocybin’s Effects
While the exact mechanisms are still under investigation, researchers believe that psilocybin’s effects on the brain may contribute to its efficacy in treating depression. These include:
- Altered Brain Connectivity: Psilocybin may temporarily alter neural pathways associated with negative thinking patterns and emotional regulation.
- Increased Neuroplasticity: It may promote the brain’s ability to reorganize and adapt, potentially leading to more resilient mental states.
- Ego Dissolution: The altered state of consciousness induced by psilocybin may allow individuals to gain new perspectives on their thoughts and emotions, potentially breaking free from ingrained negative thought patterns.
Future Directions and Considerations
The Ohio State study represents a significant step forward, but it’s essential to approach this research with both excitement and caution. Further studies are necessary to:
- Replicate the findings: Confirming the results in larger, more diverse populations is crucial.
- Explore long-term effects: Assessing the sustained benefits and potential for relapse is essential.
- Determine optimal treatment protocols: Refining dosing, therapeutic support strategies, and patient selection criteria is vital.
- Address potential risks and side effects: While generally well-tolerated, psilocybin can have side effects, and careful monitoring is necessary.
Conclusion
The Ohio State University study provides compelling evidence for the potential of psilocybin-assisted therapy in treating treatment-resistant depression. The remarkable 67% remission rate suggests a significant breakthrough in this area, offering new hope for those struggling with this debilitating condition. However, further research is crucial to fully understand the long-term effects, optimize treatment protocols, and ensure the safe and effective implementation of this promising therapeutic approach.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is psilocybin legal? A: No, psilocybin is currently illegal in most jurisdictions. However, research studies are being conducted under strict regulatory oversight.
Q2: Is psilocybin-assisted therapy right for everyone with depression? A: No. It is likely to be most beneficial for individuals with treatment-resistant depression who have not responded to conventional therapies. A thorough assessment by a mental health professional is essential.
Q3: What are the potential side effects of psilocybin? A: Common side effects can include nausea, anxiety, and changes in perception. Serious side effects are rare but possible, highlighting the need for careful monitoring in a controlled setting.
Q4: Where can I access psilocybin-assisted therapy? A: Currently, access is limited to research studies under strict regulatory approval. It is not available for widespread clinical use.
Q5: How long does psilocybin-assisted therapy take? A: The duration of treatment varies depending on the study protocol, but generally involves multiple sessions spaced over several weeks or months, including preparation and integration sessions alongside the psilocybin sessions.