The Brain’s Lymphatic System Explained: What is the Glymphatic System?
For centuries, scientists believed the brain was an exception to the rule – an organ devoid of a lymphatic system. But in the early 2010s, a groundbreaking discovery challenged this long-held assumption, revealing a dedicated waste-clearing system within the brain dubbed the glymphatic system. This revolutionary finding has profound implications for understanding and potentially treating a wide range of neurological disorders, from Alzheimer’s disease to traumatic brain injury.
This article delves into the fascinating world of the glymphatic system, exploring its function, significance, and the ongoing research shaping our understanding of its vital role in brain health.
Why is this important? The glymphatic system is crucial for removing metabolic waste products from the brain, preventing the build-up of toxic substances that can contribute to neurological decline. Understanding how it works, and how to optimize its function, could unlock new avenues for preventing and treating debilitating brain diseases.
What Exactly is the Glymphatic System?
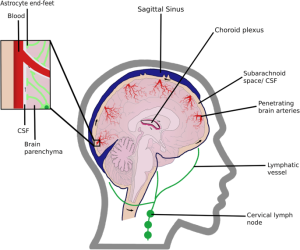
The glymphatic system is essentially the brain’s unique waste disposal system. It’s a network of perivascular spaces surrounding arteries and veins in the brain, acting as channels for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to flow through the brain tissue. Here’s how it works:
- CSF Influx: Cerebrospinal fluid, a clear fluid that cushions the brain and spinal cord, is pumped into the brain along the perivascular spaces surrounding arteries. Think of it as a refreshing cleanse.
- Interstitial Fluid Exchange: As the CSF flows through the brain tissue, it mixes with the interstitial fluid (the fluid surrounding brain cells). This exchange allows the CSF to collect waste products and toxins, such as amyloid-beta, a protein implicated in Alzheimer’s disease.
- Waste Removal: The now waste-laden fluid then drains along the perivascular spaces surrounding veins, carrying the toxins out of the brain and eventually into the lymphatic system in the body for disposal.
Think of it like a sophisticated plumbing system for the brain, ensuring a clean and healthy environment for brain cells to function optimally.
Key Components of the Glymphatic System
While the glymphatic system is a complex network, understanding its key components is crucial:
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): The lifeblood of the glymphatic system, responsible for flushing out waste.
- Perivascular Spaces: The channels surrounding arteries and veins that facilitate CSF flow.
- Astrocytes: Star-shaped brain cells that express aquaporin-4 (AQP4) water channels, playing a critical role in regulating CSF flow.
- Interstitial Fluid (ISF): The fluid surrounding brain cells, where waste exchange occurs.
The Role of Aquaporin-4 (AQP4)
Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) is a water channel protein found primarily on astrocytes, and it’s considered the key player in the glymphatic system. AQP4 facilitates the movement of water (and therefore CSF) in and out of the brain tissue, significantly enhancing the efficiency of waste clearance. Research has shown that disruptions in AQP4 function can impair glymphatic flow and lead to the accumulation of toxic waste products.
Factors Affecting Glymphatic Function
Several factors can influence the efficiency of the glymphatic system. Understanding these factors is vital for maintaining optimal brain health:
- Sleep: Studies have shown that the glymphatic system is significantly more active during sleep, highlighting the importance of adequate sleep for brain detoxification.
- Age: Glymphatic function tends to decline with age, potentially contributing to the increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases in older adults.
- Head Trauma: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) can disrupt the glymphatic system, leading to impaired waste clearance and potentially contributing to long-term neurological problems.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the brain can impair glymphatic function and exacerbate the accumulation of toxic waste products.
- Body Position: Research indicates that sleeping on your side may be more beneficial for glymphatic function compared to sleeping on your back or stomach.
Why is the Glymphatic System Important?
The glymphatic system plays a crucial role in maintaining brain health and preventing neurological disorders. Its key functions include:
- Waste Removal: Clearing metabolic waste products and toxins from the brain.
- Nutrient Delivery: Facilitating the distribution of nutrients to brain cells.
- Immune Response: Supporting the brain’s immune defense mechanisms.
- Prevention of Neurodegenerative Diseases: Reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and other neurological disorders by preventing the buildup of toxic proteins.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
The discovery of the glymphatic system has sparked a flurry of research aimed at understanding its intricacies and developing strategies to enhance its function. Current research areas include:
- Developing imaging techniques to assess glymphatic function in humans.
- Investigating the role of the glymphatic system in various neurological disorders.
- Identifying therapeutic targets to improve glymphatic clearance.
- Exploring lifestyle interventions (e.g., sleep, exercise) to optimize glymphatic function.
Conclusion
The glymphatic system represents a paradigm shift in our understanding of brain health. This intricate waste clearance system plays a vital role in removing toxins and maintaining a healthy brain environment. While research is still ongoing, understanding the glymphatic system and its influencing factors offers promising avenues for preventing and treating a wide range of neurological disorders. Prioritizing sleep, managing inflammation, and adopting a healthy lifestyle may be crucial steps in supporting optimal glymphatic function and safeguarding brain health for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How can I improve my glymphatic system function?
Prioritize getting 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Manage stress through relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga. Engage in regular physical exercise. Maintain a healthy diet rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory foods. Consider sleeping on your side.
2. Is there a way to measure glymphatic function?
Currently, measuring glymphatic function in humans is challenging. Researchers are developing advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI-based methods, to assess glymphatic flow, but these are primarily used in research settings.
3. What happens if the glymphatic system isn’t working properly?
Impaired glymphatic function can lead to the accumulation of toxic waste products in the brain, increasing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. It can also contribute to cognitive decline, inflammation, and other neurological problems.
4. Are there any medications that can improve glymphatic function?
Currently, there are no specific medications designed solely to enhance glymphatic function. However, some medications that reduce inflammation or improve sleep may indirectly benefit the glymphatic system. Further research is needed to identify potential therapeutic targets.
5. Is the glymphatic system the same as the lymphatic system in the rest of the body?
While the glymphatic system functions similarly to the lymphatic system in the body (removing waste), it is a distinct system specific to the brain. The glymphatic system utilizes CSF and perivascular spaces instead of lymphatic vessels, which were previously thought to be absent in the brain.