The Project Costing Template in Excel That Will Save You Time
Are you tired of project cost overruns, budget headaches, and the general chaos that can come with managing project finances? You’re not alone! Accurate project costing is the cornerstone of successful project management, and a well-structured Excel template can be your secret weapon. This article will guide you through the creation and utilization of a project costing template in Excel, empowering you to gain control of your project budgets and ultimately, save you valuable time and resources.
Why Excel is Your Project Costing Champion
While dedicated project management software offers robust features, Excel remains a powerful and accessible tool for project costing, especially for smaller to medium-sized projects. Its flexibility, widespread availability, and ease of use make it an ideal starting point for:
- Budget Creation: Define your project’s financial boundaries.
- Cost Tracking: Monitor actual spending against your planned budget.
- Variance Analysis: Identify discrepancies and understand the root causes.
- Reporting & Analysis: Generate insightful reports to inform decision-making.
- Customization: Tailor the template to your specific project needs and industry.
Building Your Project Costing Template in Excel: Step-by-Step
Creating a robust project costing template involves several key components. Here’s a breakdown of how to build one:
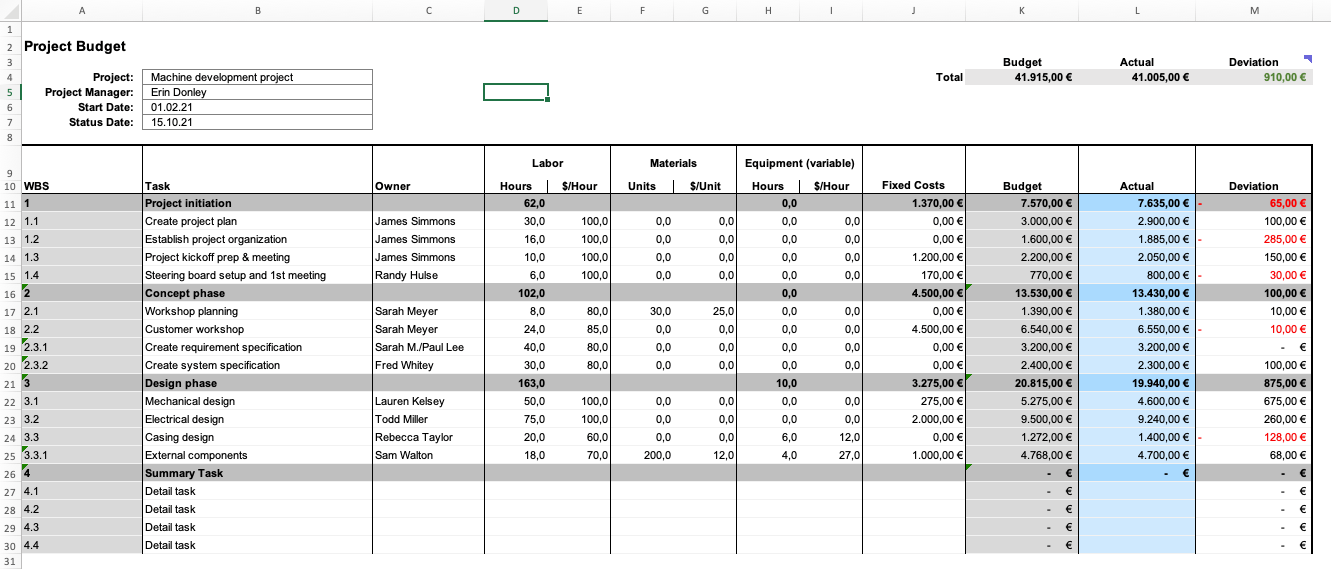
1. Setting Up Your Structure: The Foundation
Begin by establishing the basic structure of your template. Consider these essential columns:
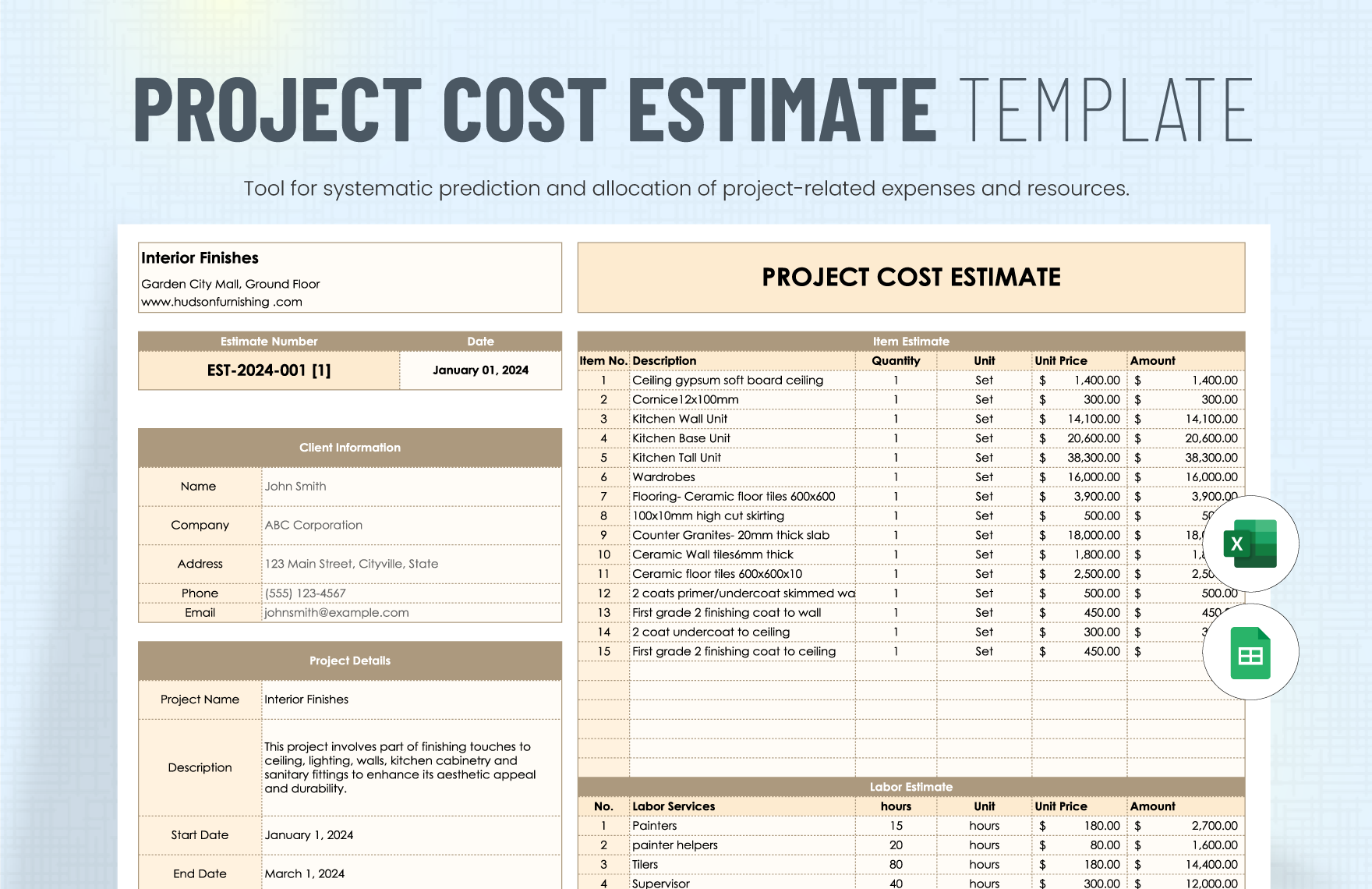
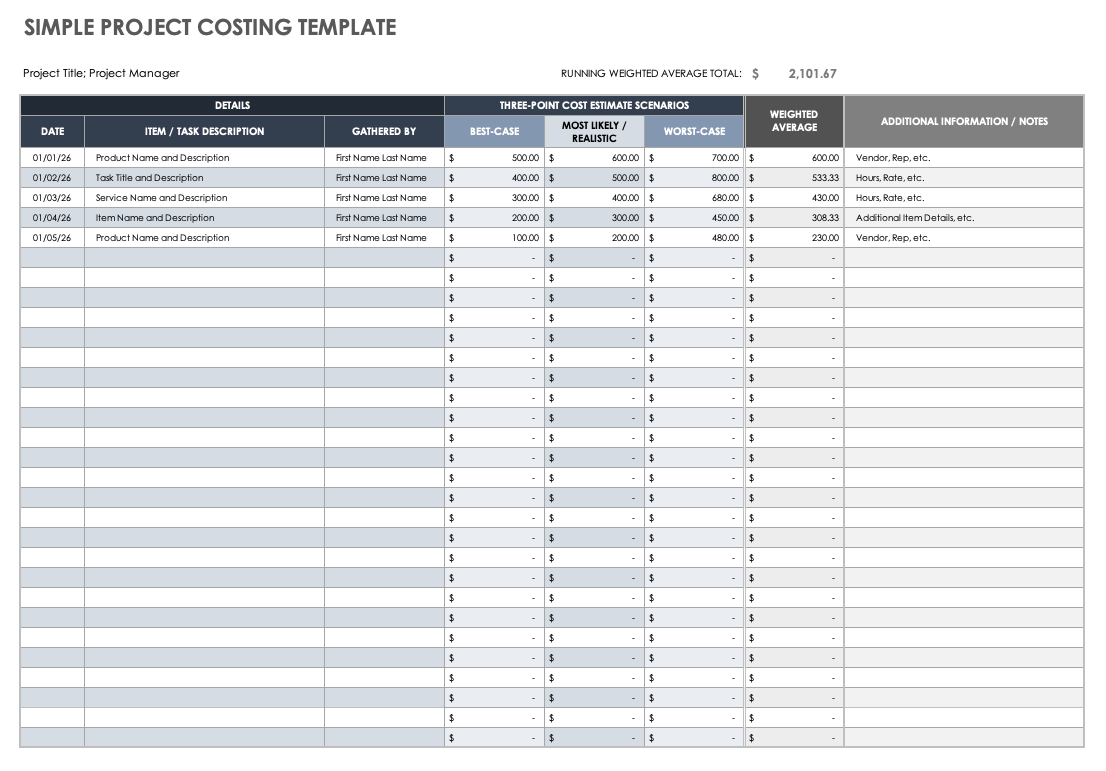
- Task/Activity: A brief description of each project element (e.g., “Website Design,” “Marketing Campaign,” “Travel Expenses”).
- Category: Group similar costs together (e.g., “Labor,” “Materials,” “Marketing,” “Travel”).
- Description: Provide a more detailed explanation of each cost.
- Planned Units: The quantity of resources needed (e.g., hours, units, days).
- Unit Cost: The cost per unit (e.g., hourly rate, cost per item).
- Planned Cost: Calculated as Planned Units * Unit Cost.
- Actual Units: The actual quantity of resources used.
- Actual Cost: Calculated as Actual Units * Unit Cost.
- Variance: Calculated as Actual Cost - Planned Cost. This reveals discrepancies between planned and actual spending.
- Notes/Comments: Space for explanations, justifications, and observations.
2. Populating the Data: Planning and Budgeting
- Identify all Project Activities: Brainstorm and list every task required to complete your project.
- Categorize Your Costs: Group similar expenses to enable easy analysis. Common categories include:
- Labor (salaries, contractor fees)
- Materials (raw materials, supplies)
- Equipment (rental, purchase)
- Travel (transportation, accommodation)
- Marketing (advertising, promotion)
- Other (permits, licenses, etc.)
- Estimate Your Resources: Determine the number of units (hours, items, etc.) required for each activity.
- Determine Unit Costs: Research and input the cost per unit for each resource.
- Calculate Planned Costs: Use Excel formulas (e.g.,
=D2*E2) to automatically calculate the planned cost for each activity. - Set Up Formulas for Totals: Use the
SUMfunction (e.g.,=SUM(F2:F10)) to calculate the total planned cost for each category and for the entire project.
3. Tracking Actual Costs: The Monitoring Phase
- Enter Actual Units Used: As the project progresses, record the actual quantity of resources used for each activity.
- Input Actual Costs: Enter the actual costs incurred for each activity, updating the unit costs if needed.
- Calculate Actual Costs: Use Excel formulas (e.g.,
=G2*E2) to automatically calculate the actual cost for each activity. - Calculate Variance: Use Excel formulas (e.g.,
=H2-F2) to calculate the variance, highlighting overspending (positive variance) or underspending (negative variance).
4. Leveraging Excel’s Power: Formatting, Formulas, and Features
- Conditional Formatting: Use conditional formatting to highlight variances. For example, color-code cells where the variance exceeds a certain threshold (e.g., red for overspending above 10%).
- Data Validation: Implement data validation rules to ensure data accuracy and consistency (e.g., restricting the input in the “Unit Cost” column to numeric values only).
- Charts and Graphs: Create charts (e.g., bar charts, pie charts) to visually represent your budget, actual costs, and variances. This will help you quickly identify trends and areas of concern.
- Filters and Sorting: Utilize Excel’s filtering and sorting capabilities to easily analyze your data by category, activity, or variance.
5. Regular Review and Adaptation: The Key to Success
- Regular Updates: Update your template regularly (weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly) to reflect actual spending and progress.
- Analyze Variances: Investigate significant variances to understand the reasons behind them.
- Make Adjustments: If necessary, adjust your budget and plan based on your findings. This iterative process is crucial for effective project cost management.
- Document Everything: Keep notes on any changes made and the reasoning behind them.
Conclusion: Unlock Project Success with Excel
A well-crafted project costing template in Excel is a powerful tool for managing your project budgets, tracking expenses, and ensuring financial control. By following these steps and actively monitoring your project’s financial performance, you can significantly reduce the risk of overspending, improve project profitability, and ultimately, save valuable time and resources. Start building your template today and experience the benefits of proactive project cost management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is Excel the best option for all projects?
No, Excel is best suited for smaller to medium-sized projects or for initial budget planning. For larger, more complex projects with multiple stakeholders and intricate workflows, dedicated project management software might be a more appropriate choice.
2. How often should I update my Excel template?
The frequency of updates depends on the project’s duration and the level of detail needed. For shorter projects or projects with tight budgets, weekly updates are recommended. For longer projects, bi-weekly or monthly updates might suffice.
3. Can I share my Excel template with other team members?
Yes, you can. However, be mindful of data security and access control. Consider using a shared drive (e.g., Google Drive, SharePoint) or using password protection to restrict unauthorized access. Also, ensure that all team members understand how to input data correctly to maintain data integrity.
4. How can I improve the accuracy of my cost estimates?
Thorough research is key. Gather quotes from vendors, review historical project data, and consult with experts in relevant fields. Also, incorporate a contingency fund (e.g., 5-10% of the total budget) to account for unexpected expenses.