The Project Management Project Template That Works Every Time: A Blueprint for Success
In the fast-paced world of project management, consistency and efficiency are key. Every project, regardless of its scope or complexity, benefits from a well-defined structure. This is where a robust project template comes into play. Forget reinventing the wheel with each new undertaking. This article will guide you through the creation and utilization of a versatile project management template, a blueprint that, when implemented correctly, can significantly increase your project success rate, reduce wasted time, and ensure consistent delivery. We’ll explore the essential elements and how to tailor the template to fit your needs, not just a generic one-size-fits-all approach.
Why You Need a Project Management Template
Before diving into the specifics, let’s understand the core benefits of having a standardized project template:
- Increased Efficiency: A template pre-populates essential elements, saving valuable time at the project initiation phase.
- Improved Consistency: Ensures all projects are managed using a consistent approach, leading to predictable results.
- Reduced Risk: Includes pre-defined processes for risk assessment and mitigation, minimizing potential setbacks.
- Enhanced Communication: Provides a framework for clear communication and collaboration among team members.
- Simplified Onboarding: Makes it easier for new team members to understand the project’s structure and their roles.
- Better Reporting: Facilitates standardized reporting, allowing for easier tracking of progress and performance.
- Facilitates Scalability: Makes it easier to handle multiple projects and allows project managers to scale their teams.
Building Your All-Encompassing Project Template: The Core Components
Creating a truly effective project template requires a holistic approach. Here’s a breakdown of the essential components you should include:
1. Project Charter & Scope Definition
- Project Title: Clearly define the project’s name.
- Project Goals & Objectives: What are you trying to achieve? Make them SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound).
- Project Scope: Define what’s included and excluded from the project. This is crucial for managing expectations.
- Key Deliverables: List the tangible outputs of the project.
- Project Assumptions & Constraints: Identify any assumptions you’re making and any limitations that might affect the project (budget, resources, deadlines).
- Stakeholder Identification: List key stakeholders and their roles and responsibilities.
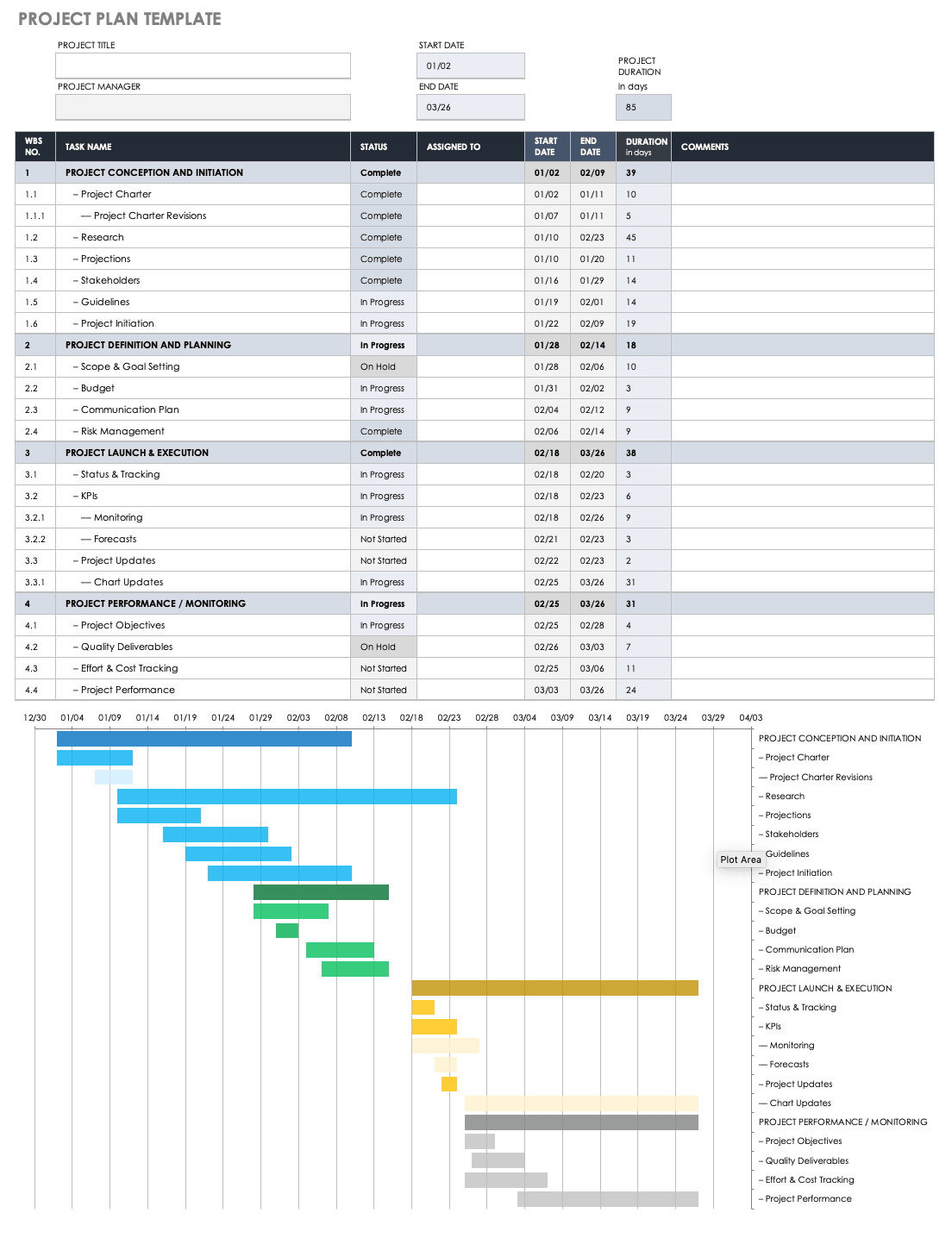
2. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Decomposition: Break down the project into manageable tasks and subtasks.
- Hierarchical Structure: Organize tasks logically, often using a numbering system (e.g., 1.0, 1.1, 1.2).
- Task Descriptions: Provide clear and concise descriptions of each task.
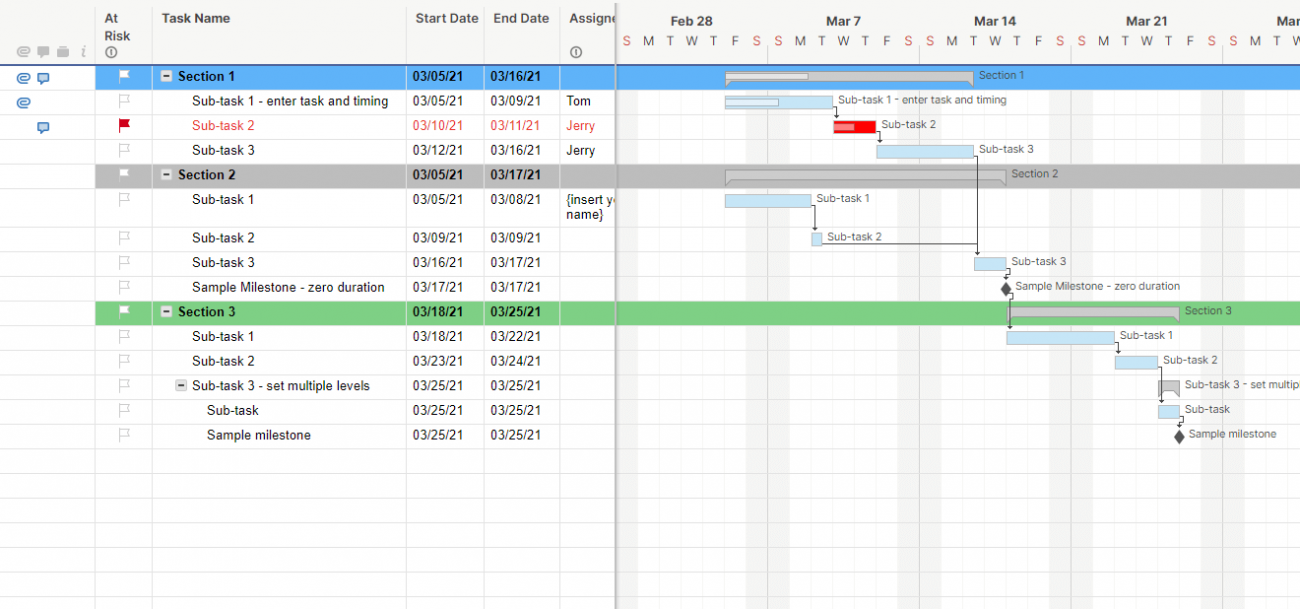
3. Project Schedule & Timeline
- Task Dependencies: Define the relationships between tasks (e.g., start-to-start, finish-to-finish).
- Estimated Durations: Estimate the time required to complete each task.
- Milestones: Identify key checkpoints and deadlines.
- Gantt Chart: Visualize the project schedule using a Gantt chart or similar visual tool.
- Resource Allocation: Assign resources (people, equipment, etc.) to specific tasks.
4. Risk Management Plan
- Risk Identification: Identify potential risks (e.g., technical issues, resource constraints, market changes).
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate the likelihood and impact of each risk.
- Risk Response Strategies: Develop plans to mitigate, avoid, transfer, or accept each risk.
- Risk Register: Document all identified risks, their assessments, and response plans.
5. Communication Plan
- Communication Frequency: Define how often project updates will be shared.
- Communication Methods: Specify the channels for communication (e.g., email, meetings, project management software).
- Communication Roles & Responsibilities: Clearly outline who is responsible for communicating what information.
- Reporting Templates: Use templates for status reports, meeting minutes, and other communication documents.
6. Budget & Cost Management
- Budget Breakdown: Allocate funds to specific tasks and resources.
- Cost Tracking: Monitor project spending against the budget.
- Variance Analysis: Identify and explain any discrepancies between planned and actual costs.
- Change Management Process: Establish a process for handling budget changes.
7. Quality Management
- Quality Standards: Define the quality standards that the project must meet.
- Quality Control Processes: Outline the processes for ensuring quality throughout the project lifecycle.
- Testing Procedures: Specify the testing methods to be used to verify deliverables.
- Review Checklists: Use checklists to ensure that deliverables meet quality requirements.
Customizing Your Template: Tailoring for Success
The beauty of a project management template lies in its adaptability. Here’s how to tailor it to your specific needs:
- Project Type: Consider the type of projects you typically manage (e.g., software development, construction, marketing campaigns). Adjust the template to fit the specific methodologies (Agile, Waterfall, etc.) and requirements of each project type.
- Industry: Different industries have different standards and best practices. Incorporate industry-specific elements into your template.
- Company Culture: Reflect your company’s communication style, decision-making processes, and preferred project management tools.
- Project Size and Complexity: Scale the level of detail in your template based on the size and complexity of the project. A small, simple project requires less detail than a large, complex one.
- Feedback and Iteration: Regularly review and update your template based on feedback from project teams and lessons learned from past projects.
Implementing and Maintaining Your Project Template
- Training: Provide training to your team on how to use the template effectively.
- Tool Integration: Integrate the template with your project management software (e.g., Asana, Trello, Microsoft Project, Jira).
- Version Control: Maintain version control of your template to track changes and ensure consistency.
- Regular Reviews: Schedule periodic reviews of the template to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
Conclusion: The Power of a Project Management Blueprint
A well-crafted project management template is more than just a document; it’s a strategic asset. By implementing and consistently using a template, you can streamline your projects, improve efficiency, minimize risks, and ultimately, achieve greater success. Invest the time upfront to create and refine your template, and you’ll reap the rewards in improved project outcomes and a more organized, productive work environment. The key is to adapt, iterate, and continually strive for improvement, ensuring your template remains a valuable tool for all your project endeavors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Where should I store my project template?
Store your project template in a central, accessible location that is easily accessible to all project team members. This could be a shared drive, a project management software platform, or a cloud-based document storage service. Ensure version control is in place.
2. How often should I update my project template?
Regularly review your template after each project, or at least quarterly. Incorporate lessons learned, industry best practices, and any changes in your company’s processes or tools.
3. What if my project requires significant deviations from the template?
The template is a starting point. It’s designed to be adaptable. Document any deviations and the reasons for them. This information can be used to improve the template in future iterations.
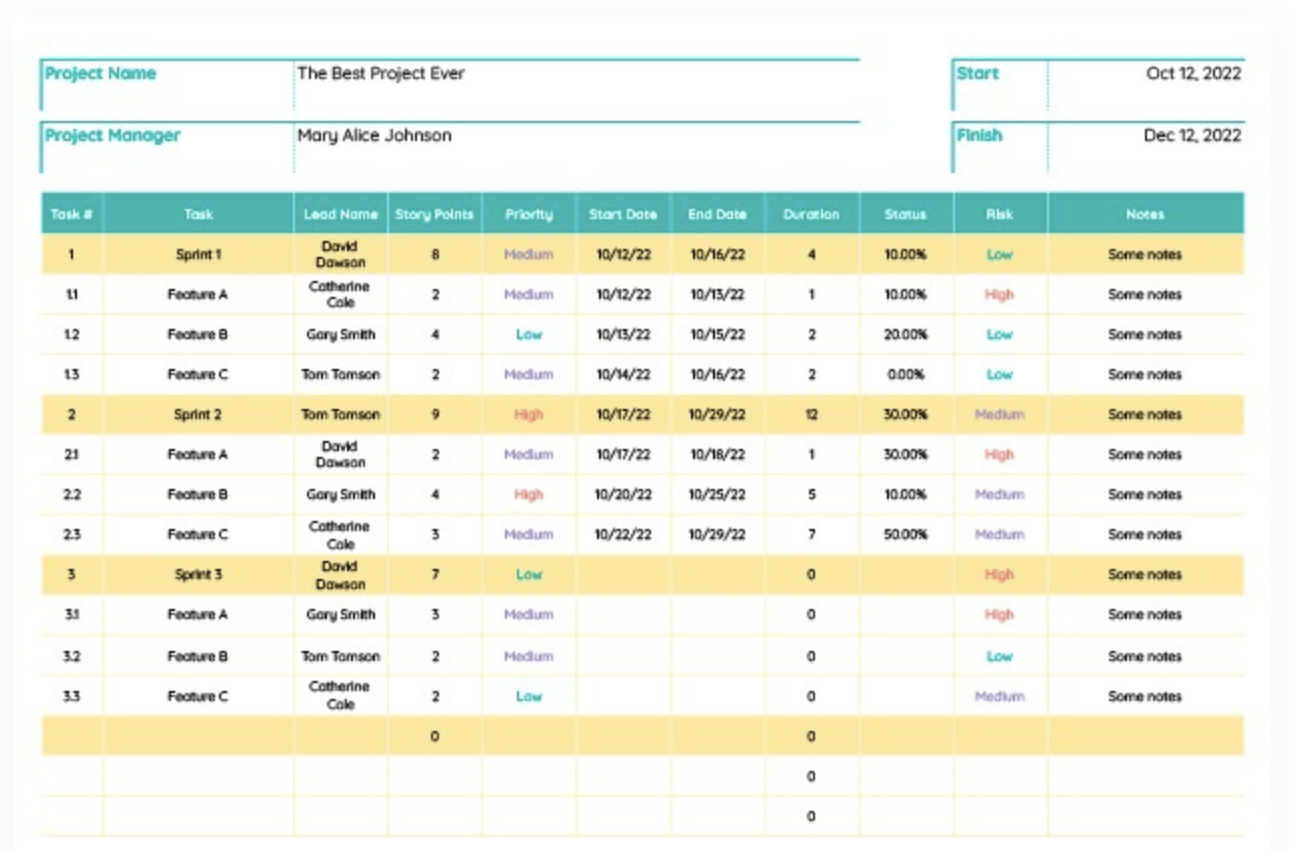
4. Can I use the template for agile projects?
Absolutely! The core components apply. Adapt the template to incorporate agile methodologies like sprints, daily stand-ups, and iterative development cycles. Focus on incorporating elements that support collaboration, flexibility, and rapid feedback.