The YTD P&L Template You’ll Ever Need: Streamlining Your Financial Performance Analysis
Are you drowning in spreadsheets, struggling to get a clear picture of your year-to-date (YTD) financial performance? Understanding your YTD Profit and Loss (P&L) is crucial for making informed business decisions, identifying trends, and ultimately, driving profitability. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the YTD P&L template, equipping you with the tools and knowledge to effectively track, analyze, and improve your financial performance. We’ll cover the key components, best practices, and even a few frequently asked questions to help you master this essential financial statement.
What is a YTD P&L and Why is it Important?
A Year-to-Date (YTD) Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, also known as an income statement, summarizes your company’s financial performance from the beginning of the current fiscal year up to a specific date. It essentially shows you:
- Your Revenues: How much money your business has generated.
- Your Expenses: The costs associated with running your business.
- Your Profit or Loss: The difference between your revenues and expenses, revealing your financial bottom line.
The importance of a YTD P&L cannot be overstated:
- Performance Tracking: It allows you to monitor your financial progress throughout the year.
- Trend Identification: You can spot emerging patterns in your revenue and expenses, helping you make proactive adjustments.
- Decision Making: It provides critical data for making informed decisions about investments, pricing, cost control, and resource allocation.
- Investor & Lender Reporting: Essential for reporting to investors and lenders who rely on this information.
- Budgeting & Forecasting: Serves as a foundation for creating accurate budgets and financial forecasts.
Key Components of a Powerful YTD P&L Template
A well-designed YTD P&L template should include the following core elements:
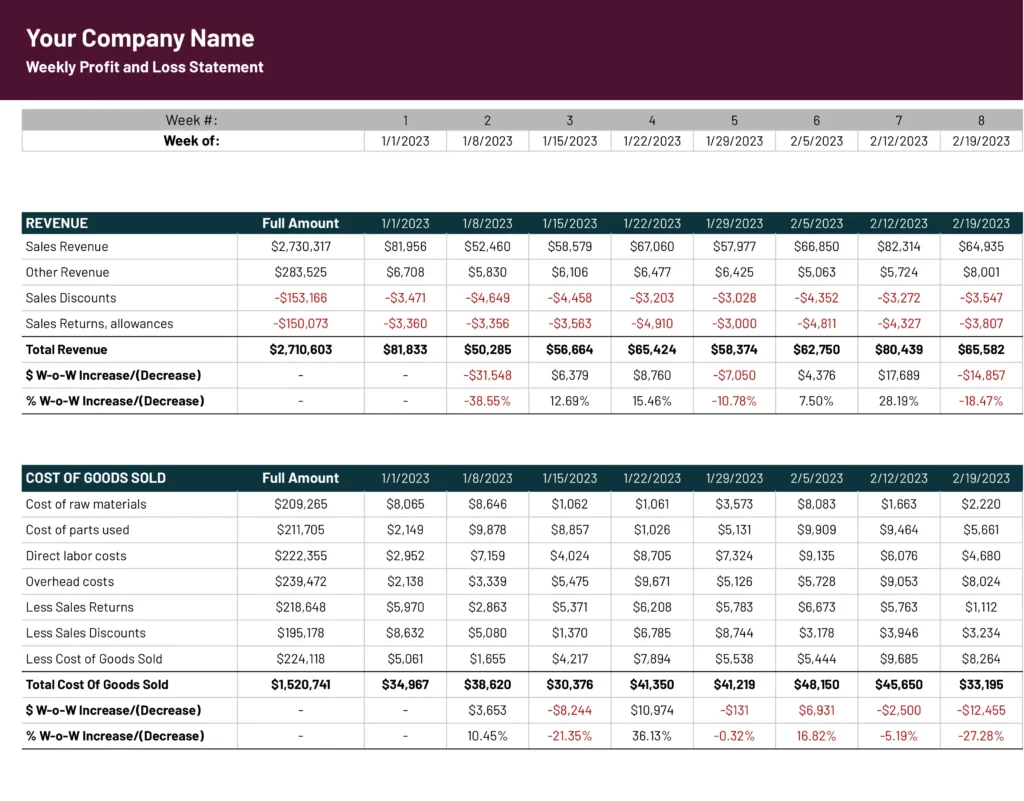
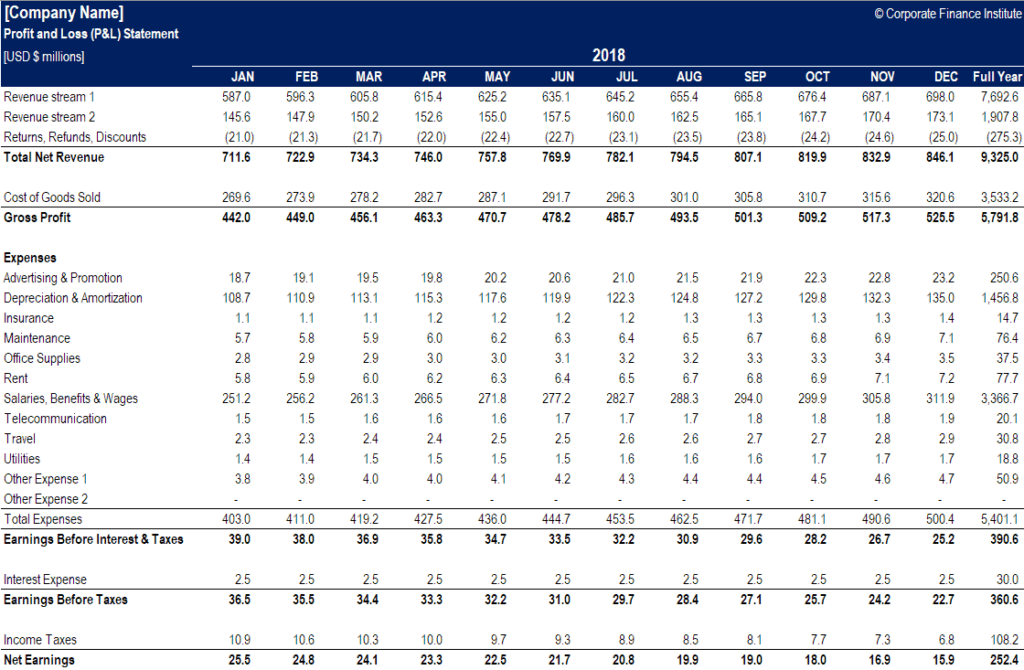
- Revenue:
- Sales Revenue: Revenue generated from the sale of goods or services.
- Other Revenue (if applicable): Revenue from sources like interest, royalties, etc.
- Total Revenue: Sum of all revenue streams.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Direct costs associated with producing goods or services, including:
- Direct Materials: Raw materials used in production.
- Direct Labor: Wages of employees directly involved in production.
- Manufacturing Overhead: Indirect costs associated with production, such as rent, utilities, and depreciation of production equipment.
- Gross Profit: Total Revenue - COGS
- Operating Expenses: Expenses related to running the business, including:
- Sales and Marketing Expenses: Advertising, marketing salaries, sales commissions.
- General and Administrative Expenses: Salaries, rent, utilities, office supplies, insurance, etc.
- Research and Development (R&D) Expenses: Costs associated with developing new products or services.
- Operating Income (EBIT - Earnings Before Interest and Taxes): Gross Profit - Operating Expenses
- Other Income and Expenses: Income or expenses not directly related to the core business operations, such as:
- Interest Expense: Cost of borrowing money.
- Interest Income: Income earned from interest-bearing accounts.
- Other Income/Expenses: Unusual or infrequent items that don’t fit elsewhere.
- Income Tax Expense: Taxes owed on the company’s profits.
- Net Income (Net Profit): The final profit or loss after all expenses and taxes are accounted for.
Building Your YTD P&L Template: Software and Best Practices
You can create a YTD P&L template using various tools, depending on your needs and resources:
- Spreadsheet Software (Excel, Google Sheets): Offers flexibility and control. Excellent for small businesses and those seeking customization.
- Accounting Software (QuickBooks, Xero, FreshBooks): Automates many aspects of financial reporting, including generating YTD P&Ls. Ideal for businesses of all sizes, especially those with complex transactions.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems (SAP, Oracle): Comprehensive systems offering advanced financial reporting capabilities. Suited for large enterprises.
Best Practices for Template Creation and Management:
- Accuracy is Paramount: Ensure all data is accurate and up-to-date. Double-check entries and reconcile accounts regularly.
- Consistent Formatting: Use a standardized format for all financial statements to improve readability and comparison.
- Detailed Breakdown: Provide a clear breakdown of revenue and expenses. Use subcategories to gain deeper insights.
- Comparative Analysis: Include columns for prior year (PY) or budget figures to facilitate comparison and trend analysis.
- Regular Updates: Update your YTD P&L at least monthly, or more frequently (weekly or even daily) depending on the pace of your business.
- Automation Where Possible: Integrate your template with your accounting software to automate data entry and reduce errors.
- Review and Analysis: Don’t just create the template; actively review the results, identify key trends, and take corrective action as needed.
Analyzing Your YTD P&L: Key Metrics and Insights
Once you have your YTD P&L in place, it’s time to analyze the data to gain valuable insights. Focus on these key metrics:
- Gross Profit Margin: (Gross Profit / Total Revenue) * 100. Indicates profitability on each sale before operating expenses.
- Operating Profit Margin: (Operating Income / Total Revenue) * 100. Reflects profitability after accounting for operating expenses.
- Net Profit Margin: (Net Income / Total Revenue) * 100. The overall profitability of your business.
- Revenue Growth: Compare current year revenue to prior year revenue or budget to assess growth.
- Expense Control: Track individual expense categories and identify areas where costs can be reduced.
- Variance Analysis: Compare actual results to your budget to identify significant variances and understand their causes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How often should I update my YTD P&L?
The frequency depends on your business needs. Monthly updates are generally sufficient, but for fast-growing or complex businesses, weekly or even daily updates may be necessary. This allows for more timely insights and proactive decision-making.
2. What’s the difference between a YTD P&L and a Balance Sheet?
The YTD P&L (Income Statement) reports a company’s financial performance over a specific period (e.g., January 1st to December 31st). The Balance Sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time (e.g., December 31st).
3. How can I use my YTD P&L to improve my business?
By analyzing your YTD P&L, you can:
- Identify underperforming revenue streams.
- Pinpoint areas where expenses are too high.
- Make informed decisions about pricing and cost control.
- Track the effectiveness of marketing and sales initiatives.
- Improve your overall profitability and cash flow.
- Forecast your future performance.
4. Can I customize the YTD P&L template to fit my specific industry?
Yes, absolutely. Adapt the template to reflect the specific revenue streams, cost structures, and reporting needs of your industry. For example, a manufacturing company will need to detail COGS more extensively than a service business.
5. What if I don’t have accounting experience?
If you lack accounting expertise, consider using accounting software that automates many of the calculations. Alternatively, consult with a qualified accountant or bookkeeper to ensure your YTD P&L is accurate and compliant.
Conclusion: Mastering Your Financial Future
The YTD P&L template is a powerful tool for understanding and managing your business’s financial performance. By implementing the strategies and best practices outlined in this article, you can gain valuable insights, make informed decisions, and drive your business towards greater profitability and success. Take control of your financial data today and unlock the potential for a brighter financial future.